Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the global prevalence of diabetes in adults over the age of 18 is steadily increasing, and it is estimated that around 8.5% of the global population has diabetes. As the number of individuals living with diabetes rises, the importance of effective diabetes management cannot be overstated. Managing diabetes involves controlling blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and minimizing the risk of complications. In this blog post, we’ll explore essential tips for managing diabetes effectively, improving quality of life, and preventing long-term health problems.
Understanding Diabetes and Blood Sugar Levels
Before diving into the tips for managing diabetes, it’s important to understand what diabetes is and how blood sugar levels play a role in the condition.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a group of diseases that result in high blood sugar (glucose) levels. This happens when the body is either unable to produce enough insulin or it cannot properly use the insulin it does produce. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy. Without adequate insulin or a proper response to insulin, blood sugar levels remain elevated.
There are two primary types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes must take insulin daily.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin. Type 2 diabetes is often linked to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity. While it can be managed through lifestyle changes, medication or insulin therapy may also be required.
- Gestational Diabetes: This type occurs during pregnancy and is typically temporary. However, women who experience gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
The Importance of Blood Sugar Management
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is essential for individuals living with diabetes. High blood sugar (hyperglycemia) over time can lead to a range of serious health problems, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, vision problems, and poor wound healing. Conversely, low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can also be dangerous, leading to symptoms like dizziness, confusion, and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness.
Managing blood sugar levels is a delicate balance, and it is crucial to keep blood sugar within a target range to prevent both short-term and long-term complications.
Key Tips for Managing Diabetes and Blood Sugar Levels
1. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
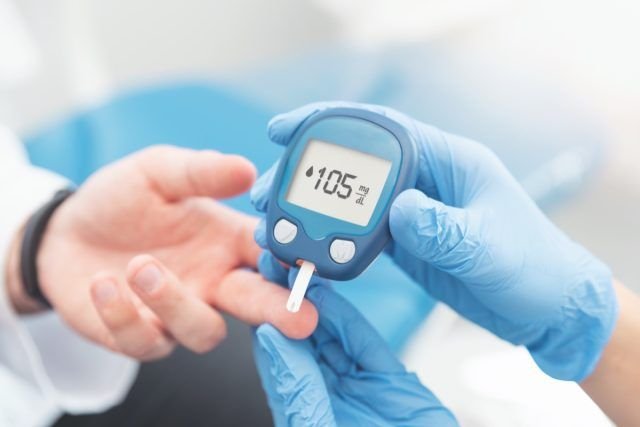
One of the most effective ways to manage diabetes is by monitoring blood sugar levels consistently. Regular testing allows you to track your glucose levels throughout the day and adjust your diet, exercise, or medication as needed.
- Use a glucometer: A glucometer is a portable device that allows you to check your blood sugar levels by pricking your finger for a small blood sample. By checking your blood sugar levels before and after meals, as well as at various times throughout the day, you can determine how food, exercise, and medication are impacting your glucose levels.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): For those who prefer more convenience and accuracy, continuous glucose monitors can be used. These devices measure glucose levels in real-time, sending data to a mobile app, allowing for more consistent tracking and fewer finger pricks.
2. Eat a Balanced, Diabetes-Friendly Diet
What you eat has a significant impact on your blood sugar levels. A healthy and well-balanced diet is essential for diabetes management. Here are some key principles for creating a diabetes-friendly diet:
- Focus on whole foods: A healthy diet should include plenty of vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Fiber-rich foods such as leafy greens, whole grains, legumes, and berries can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Carb counting: Since carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar, it’s important to manage your carbohydrate intake. Carb counting involves tracking the number of carbohydrates you consume at each meal. A healthcare provider or dietitian can help you understand how to distribute carbs throughout the day to prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Choose low glycemic index (GI) foods: Foods with a low glycemic index raise blood sugar more slowly than those with a high GI. Examples of low-GI foods include non-starchy vegetables, legumes, whole grains like quinoa and oats, and most fruits. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Limit refined sugars and processed foods: Processed foods, sugary snacks, and drinks can cause rapid increases in blood sugar levels, making it difficult to maintain control. Avoid sugary drinks, snacks, and pastries, and choose whole-food alternatives instead.
- Control portion sizes: Overeating can lead to blood sugar spikes. Be mindful of portion sizes and eat regular meals to prevent overeating. Using smaller plates and practicing portion control can help you manage your blood sugar levels.
3. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity is one of the most effective ways to manage diabetes. Regular exercise helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and allowing muscles to use glucose for energy. Exercise also helps manage weight, which is especially important for those with type 2 diabetes.
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. If you have time constraints, consider breaking the exercise into shorter 10-15 minute sessions spread throughout the day.
- Strength training: In addition to aerobic exercise, incorporating strength training (such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises) into your routine can help increase muscle mass and improve insulin sensitivity, further assisting with blood sugar management.
- Be mindful of exercise timing: If you take insulin or other medication that lowers blood sugar, exercise can sometimes cause blood sugar levels to drop too low, especially after a workout. Make sure to monitor your blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise, and carry a fast-acting carbohydrate (like glucose tablets) in case of low blood sugar.
4. Take medications as prescribed.
For individuals with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, medication is often required to manage blood sugar levels. The types of medications used for diabetes management include:
- Insulin: People with Type 1 diabetes and some people with Type 2 diabetes may need to take insulin injections to help control blood sugar levels. Insulin therapy helps the body absorb glucose into cells for energy.
- Oral Medications: There are various oral medications available for Type 2 diabetes that work in different ways, including helping the body use insulin more effectively, stimulating insulin production, or slowing the absorption of glucose from the digestive system.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Agonists: These are newer classes of drugs that help regulate blood sugar levels by either helping the kidneys excrete more glucose or improving insulin release.
It’s important to take medications as prescribed and to follow up regularly with your healthcare provider. If you experience side effects or your blood sugar levels are not well-controlled, discuss potential adjustments to your treatment plan with your doctor.
5. Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels, as it leads to the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can increase glucose production and make it harder for insulin to work effectively. Managing stress is therefore an essential part of diabetes management.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Incorporating stress-relieving activities such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, and mindfulness can help reduce stress and maintain blood sugar control.
- Engage in hobbies: Take time to engage in hobbies or activities that bring you joy, whether that’s reading, gardening, painting, or spending time with loved ones. Finding ways to relax and take your mind off daily stressors can have a positive effect on your overall well-being.
- Get enough sleep: Poor sleep can exacerbate stress and negatively affect blood sugar regulation. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Create a calming bedtime routine and avoid stimulating activities (such as using electronic devices) before bed to improve sleep quality.
6. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can lead to higher blood sugar levels, as it can cause the kidneys to work harder to filter out excess glucose. Make sure to drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated. Water also helps your body flush out excess glucose and support overall kidney function.
7. Regular Check-ups and Monitoring
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for managing diabetes and preventing complications. These visits will allow you to:
- Monitor kidney function: Diabetes can lead to kidney damage over time. Regular testing of kidney function can help detect issues early.
- Check for nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage, especially in the feet. Regular check-ups will help identify signs of neuropathy and other complications.
- Assess heart health: People with diabetes are at a higher risk of heart disease, so it’s essential to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other cardiovascular health indicators.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes requires a multi-faceted approach that combines lifestyle changes, medication, and consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels. By adopting healthy eating habits, staying active, managing stress, and following your healthcare provider’s advice, you can effectively control diabetes and minimize the risk of complications. The key is to make diabetes management a part of your daily routine and to be proactive about your health. With the right strategies in place, living with diabetes can be manageable, and you can enjoy a fulfilling and healthy life.